The consumer goods industry stands at a critical junction where technological advancements, innovation, and an evolving consumer consciousness about sustainability unite to forge a greener future. This blog explores how R&D and digital transformation play pivotal roles in reducing consumer goods' carbon footprint, helping companies cut emissions while aligning with the values of sustainability-minded consumers.
A Shifting Consumer Perspective on Sustainability
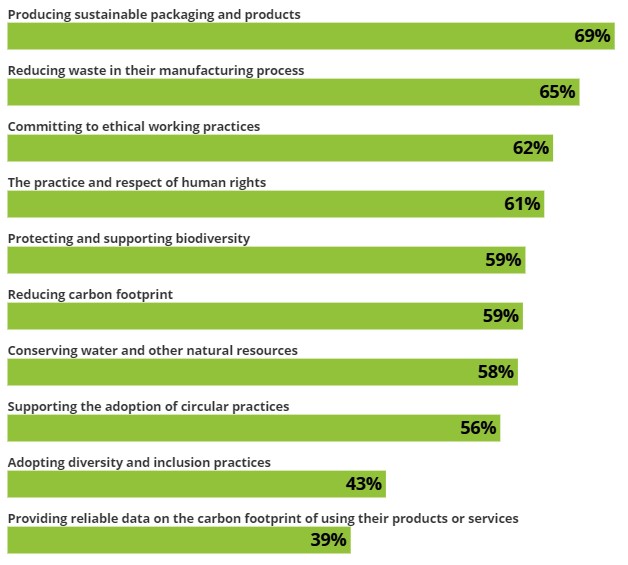
Consumer interest in sustainability is evolving beyond recycled materials or minimal packaging. The Sustainable Consumer 2023 report from Deloitte highlights a change in mindset: durability and repairability are now leading qualities that consumers associate with sustainability. Many buyers prioritize these attributes even over recyclability. Moreover, there is a growing appetite for transparency, with consumers wanting to see measurable product carbon footprint data. Notably, 16% of consumers consider this data essential when evaluating the sustainability of a product, and 11% base their purchasing decisions on its availability. Providing consumers with real-time carbon footprint data is crucial to meet this demand and foster informed decision-making.
This trend highlights the need for openness and educating consumers to support sustainable decision-making. To meet these needs, retailers and manufacturers increasingly focus on carbon labeling and circular consumer models, signaling a shift towards incorporating sustainability from R&D to product use.
Reducing Emissions Through Research and Development
R&D is at the heart of emissions reduction in consumer goods. It not only drives innovations that lower the carbon footprint during manufacturing but also reshapes the entire lifecycle of products. Companies are employing strategies like:
- Energy Efficiency Investments: Many consumer goods companies focus on improving energy efficiency, using logistics optimization tools and low-emission alternative fuels to make their supply chains leaner. This focus on operational efficiency reduces emissions and yields long-term cost savings for businesses.
- Sustainable Materials and Product Design: Material choice and product design are two areas with significant potential for lowering emissions. The United States Environmental Protection Agency shares information about raw material production, particularly in agricultural or fossil-fuel-based materials, which are often a significant source of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. R&D innovations enable companies to replace high-emission materials with alternatives such as biodegradable packaging and recycled content, which significantly lowers the environmental impact of products.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: Companies increasingly incorporate circular economy principles into their R&D efforts. Practical interventions like refill models, recycled plastic integration, and biodegradable packaging solutions support waste reduction while promoting more sustainable consumer habits. Encouragingly, one in four consumers is prepared to pay more for brands that commit to these sustainable practices, making it a moral and economic imperative for companies to invest in circular solutions.
Digital Transformation and Emission Reduction
Digital transformation offers powerful tools for decarbonization in consumer industries, enhancing visibility, efficiency, and consumer engagement:
- Green Cloud and Climate Analytics: By leveraging green cloud technologies and climate analytics, companies can monitor their emissions in real-time, optimize their operations, and engage consumers with verified information on the carbon footprint of their purchases. Tools like climate analytics drive efficient product development and supply chain decisions, reducing emissions across product lifecycles.
- Reducing the Carbon Footprint in Retail Operations: Digitalization is also streamlining retail operations, which, while not the largest source of emissions, still present opportunities for reduction. Strategic analysis from different sources shows that energy-efficient warehouses, optimized transportation, and sustainable last-mile delivery solutions significantly reduce operational emissions in the retail phase.
- Consumer Engagement through Transparency: Digital platforms have enabled consumers to access detailed product information, including real-time carbon emissions data. This level of transparency can address consumers’ need for information and foster behavioral change towards more sustainable choices.
The Consumer's Role in Carbon Reduction
Consumer behavior remains a crucial determinant in reducing the overall carbon footprint of consumer goods. Many studies are willing to investigate how consumer decisions—from the type of transportation used for the last mile to product disposal methods—can significantly impact emissions. Actions such as opting for products with lower-impact materials, minimizing product waste, and selecting energy-efficient appliances are ways in which consumers could contribute to reducing GHG emissions.
The findings from Consumer Behaviour and Sustainable Product Choices: Insights from Visual Trends reveal that consumer education and awareness should evolve to foster sustainable purchasing habits. Despite the awareness of plastic waste, some consumers favor non-reusable plastics for convenience or a need for more readily available alternatives. Addressing these challenges through better education, increased availability of other options, and enhanced transparency can help bridge the gap between awareness and action.
Furthermore, digital transformation empowers consumers to play a more active role in sustainability. Tools like carbon labeling and digital product passports allow consumers to make informed, value-based decisions, pushing the industry towards greener solutions.
The Path Forward: Innovate to Decarbonize
Innovation holds undeniable value as the consumer goods industry races to reduce emissions. By investing in sustainable business models and technologies, companies can transform into future-ready enterprises capable of meeting the growing sustainability demand for consumer goods products.
Ultimately, the journey towards a low-carbon consumer goods sector involves collaboration, innovation, and transparency. From R&D to product disposal, every stage of the product lifecycle presents opportunities for emissions reduction, and consumer industries are seizing this moment to innovate for a greener future.
Evalueserve's Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) services will help you achieve your sustainability goals at both the product and process levels, ensuring that your journey towards reduced emissions is impactful and measurable.
Talk to One of Our Experts
Get in touch today to find out about how Evalueserve can help you improve your processes, making you better, faster and more efficient.