The landscape of food production is undergoing a significant shift, driven by consumer demand for natural, minimally processed, and healthy food options. This shift necessitates a move away from synthetic additives, often perceived as artificial or detrimental to health. Plant-based alternatives are emerging as a powerful solution, offering many functional benefits derived from natural sources. Diverse applications of plant-based additives across various food production processes, exploring their potential to enhance shelf life, elevate flavor profiles, and maintain vibrant colors.
But it's not just about the end product. It’s about the process. Integrating these additives into animal-origin food products paved the way for developing healthier and more functional options for consumers. The significance of utilizing fruit and vegetable by-products as a sustainable source of bioactive compounds for future food additive development is a call to action, a reminder of our responsibility towards sustainable food production.
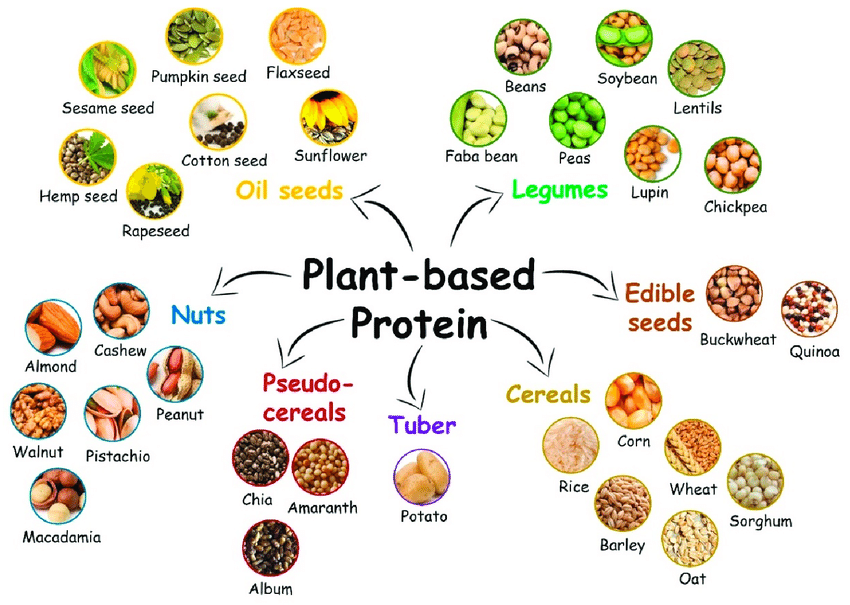
Introduction: Plant-Based Additives
The modern consumer is increasingly health-conscious and prioritizes natural ingredients over synthetic additives in their food choices. This trend is driven by concerns about the potential health risks associated with artificial additives and a demand for transparency and clean labels. The food industry is witnessing a surge in adopting plant-based alternatives that cater to this growing demand. Plant-based additives offer a unique opportunity to bridge the gap between consumer preferences and functional food production requirements.
Functionality of Plant-Based Additives
Plant-based additives offer a range of functionalities in the food industry, aiming to mimic or improve the qualities provided by animal-based ingredients.
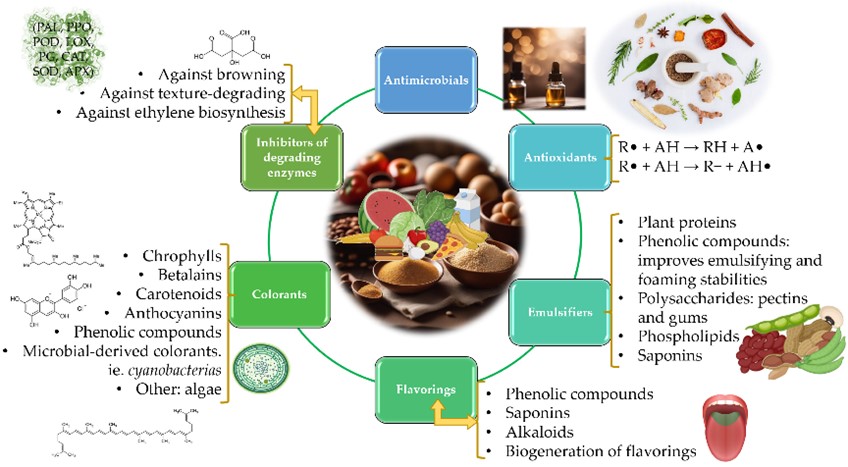
- Flavour: Plants’ inherent diversity provides a vast array of natural flavoring. Phenolic acids, for instance, contribute sour and bitter notes, while flavonoids offer a spectrum of tastes ranging from bitter and astringent to sweet. Bio-generation techniques, leveraging microbes or enzymes, further expand the palette of natural flavors, creating novel taste profiles without resorting to synthetic ingredients.
- Emulsification: Lecithin, a naturally occurring phospholipid in soybeans, flaxseed, and sunflower seeds, emerges as a powerful alternative to synthetic emulsifiers. Lecithin’s ability to stabilize oil-in-water mixtures is crucial for creating smooth and creamy textures in various products, from salad dressings and mayonnaise to baked goods and nut butter.
- Colour: Vibrant colors play a significant role in consumer perception of food freshness and appeal. Plant-based additives offer a plethora of pigments that can replace synthetic food coloring. Chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for the verdant hues of leaves, can bring a vibrant green color to food products. Carotenoids, a diverse group of pigments found in fruits and vegetables, contribute a spectrum of colors ranging from yellow and orange to red. Anthocyanins, prevalent in berries and other pigmented fruits, offer a range of blue, purple, and red hues. Extracting these pigments from plant sources provides a natural and safe alternative for coloring food products.
- Preserving Freshness Naturally: Plant extracts boast potent anti-browning and anti-texture degradation properties. Essential oils extracted from cloves and oranges exhibit remarkable effectiveness in inhibiting enzymes responsible for browning in fruits and vegetables, thus preserving their visual appeal. Similarly, essential oils derived from basil target enzymes that break down the texture of fruits and vegetables, maintaining their freshness and preventing spoilage.
- Extending Shelf Life: Extractions from readily available plants like aloe vera, lemongrass, and neem can extend the shelf life of produce, offering a promising solution that prioritizes food safety and environmental responsibility. These extracts can slow down the spoilage process in fruits and vegetables, leading to a longer shelf life and minimizing food waste.
Comparison of Natural-based Additives vs chemical-based additives
|
Feature
|
Natural Additives
|
Synthetic/chemical additives
|
|---|---|---|
|
Source
|
Derived from plants, fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices
|
Formulated and manipulated through chemical processes
|
|
Examples
|
Rosemary extract, plant essential oils (EOs), spices, natural colorants from fruits and vegetables
|
butylated hydroxy anisole (BHA), butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), sulfites, nitrates/nitrites, emulsifiers, propyl gallate, synthetic colorants, and flavorings
|
|
Safety
|
Generally regarded as safe by consumers and regulatory agencies
|
Potential health concerns linked to some additives
|
|
Functions
|
Antimicrobial, antioxidant, flavoring, coloring, emulsifying
|
Extend shelf life, reduce oxidation, enhance flavor, color food, emulsify ingredients
|
|
Regulation
|
Less strict regulations compared to synthetic additives
|
Usage limits imposed due to potential health risks
|
|
Consumer Preference
|
Align with the "Clean Label" movement for natural ingredients
|
Viewed as less desirable by some consumers due to safety concerns
|
|
Cons
|
Shorter Shelf life compared to chemical additives in some cases
|
Strong odor, color, or taste of some natural extracts may require encapsulation
|
With the growing consumer demand for natural and clean-label ingredients, the food industry is experiencing a wave of innovation in plant-based additives. These natural alternatives offer an attractive solution, replacing synthetic additives with components derived from readily available sources like fruits, vegetables, and herbs. Companies at the forefront of developing and manufacturing these plant-based solutions contribute to a more sustainable and consumer-focused food system.
Prominent examples of companies involved in the innovation of plant-based additives
Expanding the Reach: Plant-Based Innovation Reimagines Animal Origin Products
While plant-based alternatives have carved a niche for themselves in the form of meatless burgers and dairy-free milks, the innovation is extending beyond just replacements. Plant-based additives are making surprising inroads into the formulation of animal-origin food products. This integration unlocks many benefits, paving the way for a new generation of healthier and more functional animal products that cater to evolving consumer preferences.
- Functional Food: Plant-based bioactive compounds can be incorporated into animal products to create functional foods boasting a wide range of health benefits. These bioactive compounds, often derived from by-products generated by the food industry, can be introduced through animal feed or directly during processing stages. For instance, incorporating olive leaf extract into chicken feed can enhance the antioxidant profile of the resulting chicken meat.
- Clean-Label Meat Products: Aligning with Consumer Preferences, consumers are increasingly drawn to clean-label products that feature familiar ingredients and minimal processing. Replacing synthetic additives with natural plant ingredients, such as extracts, flours, concentrates, and homogenized forms derived from plants, can cater to this growing demand for transparency and clean labels in meat products.
- Lipid Profile: Substituting animal fat with fish or vegetable oils in meat products can significantly improve their overall health profile. This substitution strategy reduces saturated fatty acids and cholesterol while increasing the content of beneficial monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). This shift in the fatty acid profile can contribute to improved cardiovascular health and a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
- Antioxidant Enrichment: Plant-based antioxidants offer a natural and safe approach to reducing oxidative damage in meat products. This extends shelf life and potentially provides health benefits to consumers. Fruit residues rich in phenolic compounds, such as grape skins and pomegranate peels, are valuable natural antioxidants that can be incorporated into meat products to enhance their stability and potential health benefits.
Prominent examples of companies replacing animal-origin food with plant-based additives
Sustainability: Fruit and Vegetable By-products
Using fruit and vegetable by-products, such as skins, seeds, and leaves, presents a sustainable solution for sourcing bioactive compounds for food additives. Often discarded as waste, these by-products represent a treasure trove of valuable nutrients and bioactive compounds. Repurposing these by-products for food additive development minimizes waste generation and environmental impact associated with traditional disposal methods.
Innovation and Sustainability
As research and development in the field of plant-based additives continues to progress, several key trends are expected to shape the future:
- Biotechnology: Optimizing processes for obtaining bioactive compounds through enzymatic or microbial fermentation holds immense promise for increased efficiency and affordability. This approach leverages the power of living organisms, such as enzymes or microbes, to produce the desired compounds from plant materials. Additionally, genetically modified microorganisms might be explored to enhance production efficiency further. However, rigorous safety assessments and transparent labeling are crucial when considering genetically modified organisms in food production.
- Green Technologies: A Sustainable Approach to Extraction: Extracting and purifying bioactive compounds from plant by-products using eco-friendly technologies is paramount for sustainable production. Green technologies prioritize the use of non-toxic solvents and minimize residual waste generation. Supercritical fluid extraction, pressurized carbon dioxide, and microwave-assisted extraction are green technologies that can be harnessed for the sustainable extraction of valuable bioactive compounds from plant materials.
Moving Forward
Plant-based additives are revolutionizing the food industry. They're emerging as a natural, functional, and sustainable alternative to synthetic or chemical additives. Their versatility allows them to enhance shelf life, elevate flavor profiles, maintain vibrant colors, and promote overall food quality. Additionally, integrating these additives into animal-origin food products opens doors for development. This creates healthier and more functional options for consumers seeking such products.
Research and development are actively optimizing production processes. By delving deeper into biotechnology and green technologies, scientists make plant-based additives even more efficient. This positions natural or plant-based additives to play a central role in shaping a sustainable and healthy future for food production.
Talk to One of Our Experts
Get in touch today to find out about how Evalueserve can help you improve your processes, making you better, faster and more efficient.