As global food systems face mounting pressure from population growth, climate change, and resource scarcity, one question looms: Where will tomorrow’s protein come from? With the world population expected to hit 10 billion by 2050, traditional protein sources like beef and pork are increasingly unsustainable due to their intensive land, water, and carbon footprints.
Enter insect protein — a nutrient-rich, resource-efficient, and scalable solution gaining traction far beyond novelty snacks. Already part of the diet for over 2 billion people worldwide, edible insects are now moving from niche to mainstream, largely thanks to rapid advancements in research and development (R&D).
From genetic optimization and vertical farming to bio-based materials and waste-to-protein systems, R&D is transforming insect protein into a serious contender for global nutrition and sustainability agendas. This blog explores how cutting-edge innovations are unlocking the full potential of insect protein — and why companies at the intersection of food, biotech, and sustainability should pay close attention to the future of protein.
Nutritional Profile of Insect Protein
Macronutrient Composition
Edible insects offer impressive nutrient credentials that exceed conventional protein sources. The macronutrient profile of insect protein is vital for sustainable nutrition because of its efficient resource use and environmental advantages over traditional protein sources. Insect farming demands much less land, water, and feed than conventional livestock farming. For example, producing 1 kg of insect protein requires only a tiny fraction of the water and land needed for the same amount of beef or pork. Additionally, insect farming produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions and can use organic waste as feed, further minimizing environmental impact.
The macronutrient composition of edible insects is shown in tabular form.
|
Insect
|
Stage
|
Protein Content (%)
|
Fat Content (%)
|
Fibre Content (%)
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Silkworm
|
Pupa
|
55
|
29
|
14
|
|
Yellow mealworm
|
Larva
|
46
|
36
|
18
|
|
Western honeybee
|
Brood
|
21
|
31
|
11
|
|
Giant water bug
|
Adult
|
55
|
7
|
11
|
|
Jamaican field cricket
|
Nymph
|
65
|
34
|
8
|
Note: Values are in (g/100g dry basis)
Recent R&D efforts have highlighted the micronutrient advantages of insect protein, showcasing its potential to address nutritional deficiencies in various populations. Edible insects are notable for their rich mineral content, including iron, zinc, potassium, sodium, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, manganese, and copper. For instance, the mopane caterpillar (Gonimbrasia Belina) (31 to 77 mg per 100 g of dry matter) and grasshopper (Locusta Migratoria) (8 to 20 mg per 100 g of dry matter) contain a high iron content.
Edible insects are also rich in vitamins, including thiamine, riboflavin, and vitamin B12. They also contain retinol, β-carotene, and vitamin E. For instance, Silkworm Bombyx mori contains 9.65 mg of tocopherols per 100 g of dry matter, and yellow mealworm beetle T. molitor contains abundant Vitamin B12.
R&D Breakthroughs Driving Industry Growth
- Genetic Optimization
Breeding programs have dramatically improved insect farming economics. Developing high-yield, disease-resistant insect strains enhanced production efficiency. Aalborg University (Denmark) scientists have enhanced black soldier fly and house fly production by employing selective breeding and refining environmental conditions. These efforts have successfully facilitated the efficient transformation of organic waste into valuable products.
- Processing Innovations
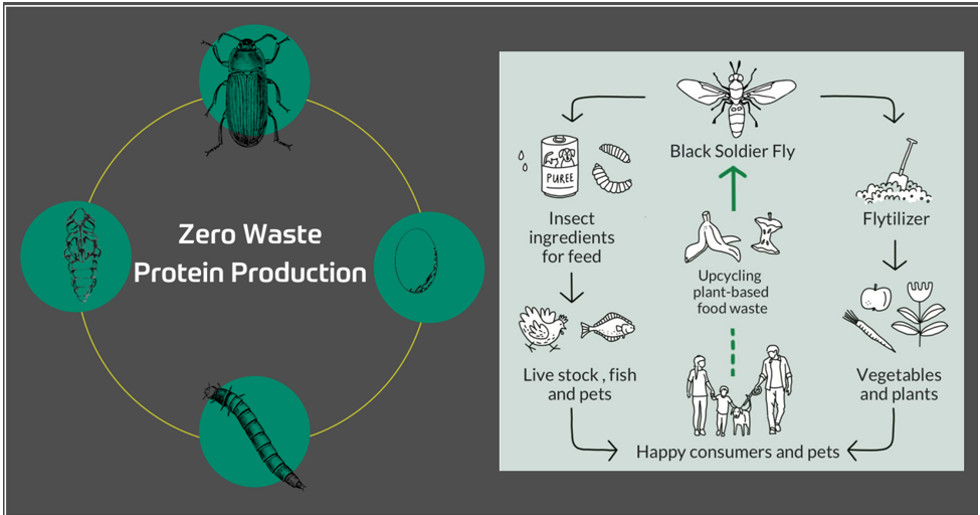
Processing innovations, driven by R&D, have revolutionized insect farming, significantly enhanced sustainability and operational efficiency, and addressed consumer acceptance barriers. Novel extraction techniques have addressed key barriers to consumer acceptance. French biotech firm Ynsect breeds mealworms for protein, which is utilized in fertilizers, livestock feed, and pet food. They have devised a method to produce biodegradable plastic by feeding black soldier flies with human waste and extracting the biological polymer chitin in a sustainable, circular process.
- Automation and Scaling
Automation and scaling have driven R&D breakthroughs by enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Automated systems streamline tasks, allowing researchers to focus on innovation. Aspire Food Group leverages innovative automation and scaling techniques to enhance insect protein production. They use robotics and automated systems to feed, monitor, and harvest crickets, ensuring precise and efficient operations. Vertical farming helps to maximize space and productivity, while data collection and machine learning provide valuable insights for continuous improvement. Their modular production system is designed for easy expansion, allowing them to scale up to meet increasing demand quickly. These innovative technologies enable Aspire to produce high-quality protein sustainably and efficiently.
The Future of Protein: Case Studies
Protix is transforming the black soldier fly industry with their insect farming technology. They produce high-quality proteins and lipids crucial for animal feeds and human nutrition. By creating a circular economy, Protix turns waste into valuable resources, promoting sustainability. Their technology features automated systems for breeding, feeding, and harvesting insects, ensuring consistent and scalable production. A key part of their circular economy model is their waste management process. Protix collects organic waste from various sources, such as food scraps and agricultural by-products. This waste is then converted into a nutrient-rich diet for the black soldier fly (BSF) larvae. The larvae efficiently transform the waste into high-quality proteins and lipids, which are harvested for use in animal feed and other products. This method reduces waste and turns it into valuable resources, promoting sustainability and reducing the environmental impact of food production.
Beta Hatch is at the forefront of transforming the insect-rearing industry through innovative technologies developed via extensive R&D that convert organic waste into valuable proteins, oils, and nutrients by raising yellow mealworms, which are highly effective at transforming waste into valuable resources. The process begins by collecting organic waste from various sources to feed the mealworms. These mealworms are then raised in a controlled environment using vertical farming techniques to maximize space and efficiency. Their decentralized production model, which includes a hub-and-spoke system, allows for flexible and scalable operations, meeting the increasing demand for sustainable protein sources. A notable feature of Beta Hatch’s technology is its integration with other industries.
Their circular production system uses waste heat from a neighbouring data centre to condition our insect grow rooms, collaborating with Washington Clean Energy to reduce energy consumption and enhance sustainability. This facility is North America’s largest mealworm production site, capable of producing a ton of insect protein daily.
Conclusion: The Way Forward to The Future of Protein
In summary, research and development (R&D) are essential for advancing insect protein as a sustainable nutrition solution. Innovative technologies are making protein production more eco-friendly and efficient. Companies like Protix and Beta Hatch are at the forefront, converting organic waste into valuable proteins and addressing the demand for sustainable sources.
As regulatory frameworks improve and consumer acceptance grows, the potential of insect protein is increasingly recognized. Businesses looking to innovate can benefit significantly from partnering with Evalueserve. Their expertise offers a comprehensive suite of services, including:
Data Analysis: Utilizing advanced analytics to derive actionable insights from large datasets, helping companies identify trends and make informed decisions.
Market Research: Conducting thorough market assessments to evaluate competition, consumer preferences, and market potential for insect protein products.
Business Strategy Development: In formulating tailored strategies that align with company goals and industry dynamics, ensuring sustained growth.
Supply Chain Optimization: Analyzing and improving supply chain efficiencies to reduce costs and enhance product delivery timelines.
Regulatory Guidance: Providing insights into compliance with regional and international regulations, helping companies navigate the legal landscape more effectively.
Innovation Support: Facilitating collaboration and ideation workshops to stimulate creativity and foster new product developments.
By collaborating with Evalueserve, companies can accelerate their insect protein initiatives, streamline operations, and position themselves as leaders in transitioning to sustainable and nutritious alternative protein sources.
Talk to One of Our Experts
Get in touch today to find out about how Evalueserve can help you improve your processes, making you better, faster and more efficient.