The European Union (EU) has again demonstrated its global leadership in technological regulation with the groundbreaking EU AI Act, which is poised to take effect next month. This pivotal decision not only represents the EU's first comprehensive endeavor to regulate artificial intelligence (AI) on a global scale but also underscores its steadfast dedication to trust, transparency, and accountability in the swiftly evolving AI landscape. By ensuring our audience is well-informed and aware of this global AI landscape, we strive to underscore the profound influence of the EU AI Act.
What Makes the AI Act Unique?
The EU AI Act distinguishes itself from other global AI regulatory approaches in many ways. The Act tackles AI's intricacies and potential risks by introducing a balanced regulatory framework and risk-based classification while avoiding innovation stifling.
- Balanced Regulatory Framework. Unlike the United States' voluntary compliance approach or China's focus on social stability, the EU's AI Act introduces strict transparency obligations for high-risk AI systems alongside lighter requirements for general-purpose AI models. This unique and balanced approach is not about stifling innovation but about fostering it responsibly and safely. It is designed to address critical concerns such as misinformation, fake news, and the misuse of copyrighted material while reassuring you, our audience, about the Act's positive impact on innovation.
- Risk-Based Classification. The Act classifies AI applications into minimal, limited, high, and unacceptable risk categories, each with tailored regulatory requirements. High-risk AI systems, such as those used in critical infrastructure, education, and employment, are subject to the most stringent rules to ensure their safety and reliability.
After examining the AI Act's unique core principles, we will discuss its specific provisions and their impacts on various sectors.
Key Provisions and Impacts
The AI Act's key provisions enhance transparency and accountability while respecting and protecting fundamental rights. These measures, pivotal in shaping a secure and innovative AI landscape, are a testament to our commitment to your well-being and dignity. They also directly and significantly impact various sectors, underlining the Act's relevance and importance in the global AI landscape.
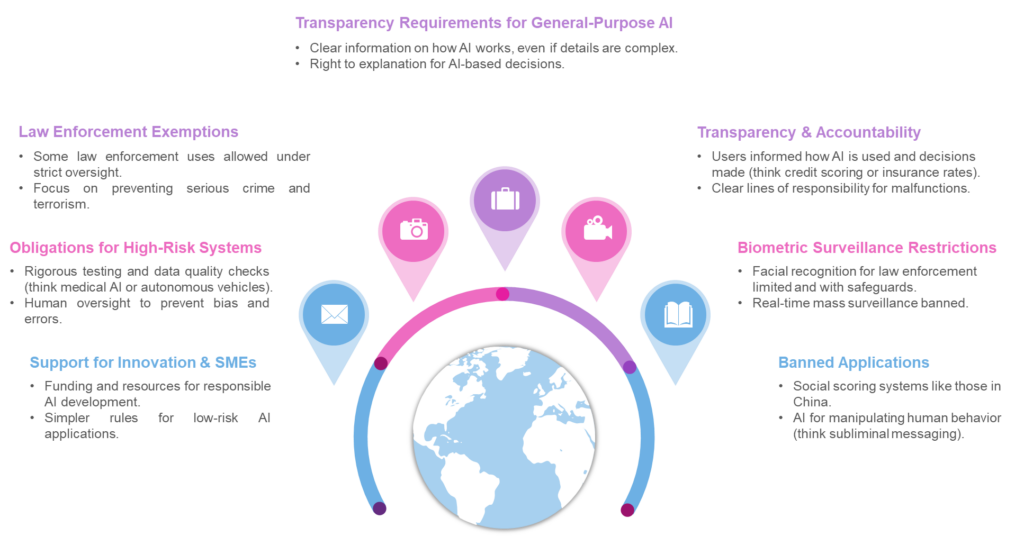
- Transparency and Accountability. The EU AI Act mandates stringent transparency requirements for high-risk AI applications. This includes the obligation for providers of these systems to disclose relevant information about the AI's functioning and decision-making processes. Such transparency fosters trust and allows for better oversight, ensuring that the operations of high-risk AI applications are understandable and accountable.
- Biometric Surveillance Restrictions. The Act significantly limits governments' real-time biometric surveillance in public spaces, restricting it to severe crimes. This provision enhances privacy protection and curbs potential abuses of surveillance technology, aligning with the EU's strong data protection and privacy stance.
- Banned Applications. The new rules ban specific AI applications that threaten citizens' rights, including biometric categorization systems based on sensitive characteristics and untargeted scraping of facial images from the internet or CCTV footage to create facial recognition databases. Emotion recognition in the workplace and schools, social scoring, predictive policing based solely on profiling, and AI that manipulates human behavior or exploits people's vulnerabilities will also be forbidden.
- Law Enforcement Exemptions. Law enforcement's use of biometric identification systems is prohibited in principle except in narrowly defined situations. Real-time biometric identification can only be deployed under strict safeguards, such as prior judicial or administrative authorization, and is limited to specific cases like searching for a missing person or preventing a terrorist attack. Post-remote biometric identification, used after the fact, is considered a high-risk application requiring judicial authorization and connection to a criminal offense.
- Obligations for High-Risk Systems. The law foresees clear obligations for other high-risk AI systems due to their significant potential harm to health, safety, fundamental rights, the environment, democracy, and the rule of law. High-risk AI uses include critical infrastructure, education, employment, essential services, and specific law enforcement and border management systems. Such systems must assess and reduce risks, maintain use logs, be transparent and accurate, and ensure human oversight. Citizens will have the right to submit complaints about AI systems and receive explanations about decisions affecting their rights.
- Transparency Requirements for General-Purpose AI. General-purpose AI (GPAI) systems must meet specific transparency requirements, including compliance with EU copyright law and publishing detailed summaries of the content used for training. The more powerful GPAI models that could pose systemic risks will face additional requirements, including performing model evaluations, assessing and mitigating systemic risks, and reporting on incidents. We must clearly label artificial or manipulated images, audio, or video content ("deepfakes").
- Support for Innovation and SMEs. The Act will establish regulatory sandboxes and real-world testing nationally to support SMEs and startups in developing and training innovative AI before its market release. Smaller enterprises can innovate within a clear regulatory framework without facing disproportionate barriers.
Driving Innovation and Ethical Standards
The AI Act encourages responsible AI innovation by establishing a transparent regulatory environment. Companies can invest in AI development more confidently, knowing their products will meet stringent ethical and safety standards. This regulatory clarity is particularly beneficial for startups and SMEs, which can navigate the AI landscape with clear guidelines.
As the world prepares to adapt to these new regulations, it is crucial to recognize the proactive measures leading organizations take in response to the AI Act.
Criticisms and Concerns
While aiming to be a world-first in regulating artificial intelligence, the EU's AI Act has attracted some criticism. Here are some of the key points:
Loopholes for Law Enforcement
Some critics argue that the Act allows law enforcement too much freedom to use specific risky AI applications, like facial recognition, in public spaces. This could lead to privacy violations and limitations on civil liberties.
Ineffectiveness of High-Risk AI
Concerns exist that the Act doesn't adequately assess or prevent risks from high-risk AI. The requirement to list risks without robust mitigation strategies is seen as insufficient.
Burden on Small Businesses
The compliance costs associated with the Act might be too high for startups and small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to handle. This could stifle innovation in the EU.
Overly Broad Definition of AI
The Act's definition of AI may be too broad, capturing even lower-risk systems that wouldn't necessarily require regulation. This creates uncertainty for businesses about what falls under the Act.
It's important to note that the Act also has defenders who argue it provides a good balance between fostering innovation and protecting citizens. The Act's flexibility and reliance on future standards aim to address some criticism.
Evalueserve's Commitment
Evalueserve is committed to following and complying with regulations worldwide in innovation, research and development (R&D), and intellectual property. We are dedicated to providing services that align with these stringent standards, ensuring our clients can confidently navigate the regulatory landscape and focus on innovation.
Looking ahead, the EU's proactive stance on AI regulation will significantly influence global practices and set a new benchmark for ethical AI development.
Looking Ahead
The EU's proactive stance sets a crucial precedent as we enter an era where AI plays an integral role in our daily lives. The AI Act addresses present challenges and prepares us for the future, ensuring that AI development aligns with ethical and societal standards.
Europe's Leadership in AI Regulation
Europe's leadership in AI regulation is a testament to its commitment to shaping a safer, more transparent, and innovative technological future. The AI Act underscores the EU's role as a global leader in technology governance, promoting a progressive and moral AI vision.
Conclusion
The EU AI Act represents a significant milestone in global AI regulation. By balancing innovation with strict regulatory oversight, the Act sets a new standard for AI governance. As the world watches the implementation of this groundbreaking legislation, it is clear that the EU is paving the way for a future where we develop and deploy AI technology responsibly, ensuring that it benefits society as a whole.
Talk to One of Our Experts
Get in touch today to find out about how Evalueserve can help you improve your processes, making you better, faster and more efficient.