The convergence of global disruptions and the pressing demand for environmental responsibility has placed supply chains under unprecedented scrutiny. The urgency of these challenges—pandemics, geopolitical instability, natural disasters, and fluctuating markets—has revealed critical vulnerabilities in traditional supply chain models. At the same time, growing consumer expectations and regulatory frameworks drive businesses to align their operations with sustainability goals.
This article provides a comprehensive framework for balancing supply chain resilience with environmental sustainability, emphasizing strategies like life cycle assessments (LCAs) and supplier-focused initiatives.
The Need for Resilient and Sustainable Supply Chains
Resilience in supply chains ensures the ability to adapt and recover from disruptions, while sustainability focuses on minimizing environmental harm. At first glance, these priorities may seem contradictory—resilience often involves redundancy, which can lead to inefficiencies, whereas sustainability emphasizes lean and efficient processes. However, when approached strategically, resilience and sustainability can complement and reinforce each other.
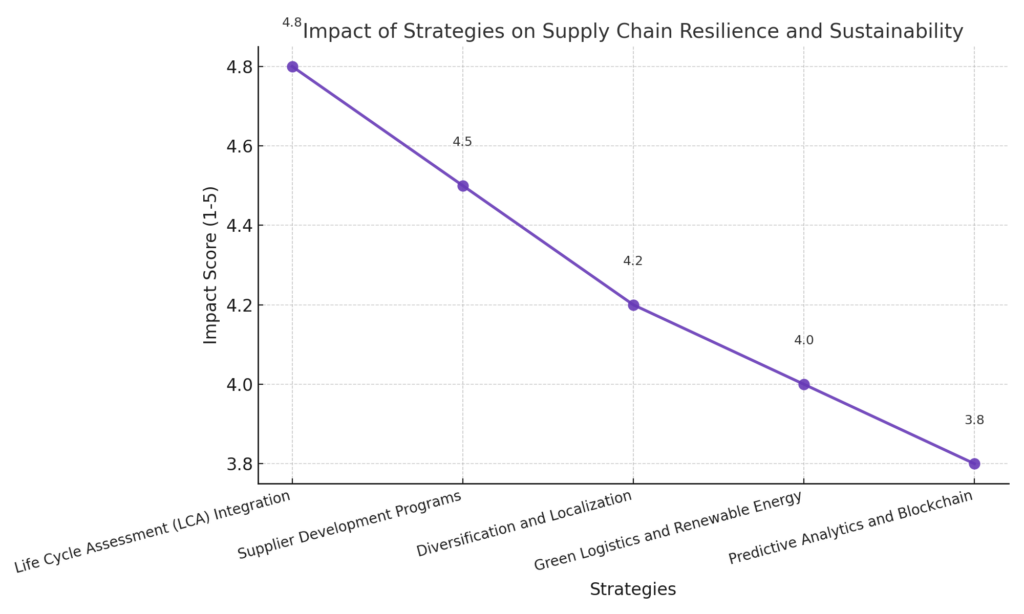
Life Cycle Assessment: A Key Tool for Supplier Evaluation
A Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) evaluates a product’s or process’s environmental impact from raw material extraction to disposal or recycling. Incorporating LCAs into supply chain management allows businesses to identify and mitigate environmental risks while choosing suppliers that align with their sustainability goals.
How LCAs Can Enhance Resilience and Sustainability
- Identify High-Impact Areas: LCAs pinpoint stages where environmental impacts are highest in the supply chain, enabling targeted interventions.
- Promote Sustainable Sourcing: Insights from LCAs can guide the selection of suppliers with lower carbon footprints and sustainable practices.
- Enhance Risk Management: By understanding environmental dependencies, businesses can anticipate disruptions (e.g., resource shortages or regulatory changes).
Example: A global electronics manufacturer used LCAs to identify that over 70% of its carbon footprint came from upstream suppliers. By partnering with renewable energy suppliers, the company reduced emissions by 30% over three years.
Supplier-Centric Strategies for Resilience and Sustainability
Suppliers are pivotal in shaping supply chains’ environmental and operational resilience. It’s crucial that businesses actively engage with their suppliers to ensure alignment with sustainability goals while enhancing adaptability. This collaborative effort is key to the success of a resilient and sustainable supply chain.
1. Sustainable Supplier Selection
Incorporating environmental criteria into supplier selection processes ensures that partners share your sustainability commitments. This approach can require renewable energy use, water conservation, and waste reduction measures.
Actionable Insight: Use LCAs during the onboarding process to evaluate the environmental impact of potential suppliers.
2. Supplier Development Programs
Empowering suppliers through training, technical assistance, and financial incentives encourages them to adopt sustainable practices. Collaborative initiatives, such as joint investments in green technologies, can yield long-term benefits for all parties.
Case Study: A major retailer funded its suppliers’ installation of energy-efficient machinery, reducing emissions across the supply chain by 15%.
3. Supply Chain Transparency and Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology allows businesses to track and verify supplier compliance with sustainability goals. Transparent supply chains reduce the risk of reputational damage from unethical or environmentally harmful practices.
Fact: According to a Purdue University report, blockchain-enabled traceability can improve supplier accountability and reduce compliance costs by 25%.
4. Diversification and Localization
Relying on a single supplier or region increases vulnerability during disruptions. Diversifying and localizing supply chains reduces environmental impact (shortening transportation distances) and enhances adaptability.
Technological Innovations Supporting Resilient, Sustainable Supply Chains
Predictive Analytics
Companies can use AI and machine learning to predict disruptions and identify opportunities to optimize supply chain operations. Predictive tools also help monitor and minimize environmental impacts.
Example: IoT sensors and advanced analytics allowed a logistics firm to reduce fuel consumption by 12%, cutting costs and emissions.
2. Renewable Energy Integration
Investing in renewable energy for manufacturing and logistics operations reduces dependency on fossil fuels, which are subject to price volatility and supply disruptions.
3. Circular Economy Principles
By designing supply chains that prioritize reuse, refurbishment, and recycling, businesses can decrease waste while ensuring consistent access to materials during supply disruptions.
Life Cycle Assessments in Action: Key Metrics and Applications
When implementing LCAs, companies should focus on these metrics:
- Carbon Footprint: Measures greenhouse gas emissions across the supply chain.
- Water Usage: Identifies high water-consuming processes or suppliers.
- Material Efficiency: Tracks resource use and waste generation.
Practical Application:
A leading consumer goods company conducted LCAs for its product lines and discovered significant environmental impacts in packaging. By switching to biodegradable materials sourced from local suppliers, the company achieved:
- 20% reduction in transportation costs.
- 35% lower carbon emissions.
- Increased resilience by reducing dependence on global supply chains.
Overcoming Challenges
Balancing resilience and sustainability is not without hurdles. Key challenges include:
- High Costs of Sustainable Practices: Upfront investments in renewable energy, green logistics, or LCA tools can be significant.
Solution: Leverage subsidies, tax credits, and sustainability-focused funding programs.
- Resistance to Change Among Suppliers: Suppliers may lack the resources or motivation to adopt sustainable practices.
Solution: Establish incentive programs, provide technical support, and foster long-term partnerships.
Benefits of a Resilient and Eco-Friendly Supply Chain
- Operational Efficiency: Sustainability initiatives often result in streamlined operations and cost savings.
- Brand Value: Consumers and stakeholders increasingly favor companies with firm environmental commitments.
- Regulatory Compliance: Proactively addressing sustainability ensures adherence to evolving environmental regulations.
- Competitive Advantage: Resilient supply chains minimize disruptions, ensuring consistent service delivery.
Conclusion
Building resilient and eco-friendly supply chains is no longer a competitive advantage but a necessity. Businesses can navigate global disruptions while achieving sustainability goals by integrating tools like Life Cycle Assessments, collaborating with suppliers, and leveraging technological innovations.
As supply chain complexities grow, the ability to align resilience with sustainability will define industry leaders. Companies that invest in these strategies now will secure operational stability and set benchmarks for responsible business practices.
Talk to One of Our Experts
Get in touch today to find out about how Evalueserve can help you improve your processes, making you better, faster and more efficient.


